Concrete and Materials Strength Laboratory

Arman Sanat Tadbir Andish Laboratory Complex consists of various sections, generally categorized into the Concrete and Building Materials Laboratory, Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Laboratory, Materials and Metallurgy Laboratory, Asphalt Laboratory, and more. In this section, we introduce the Concrete and Building Materials Laboratory.
The services of the Concrete and Building Materials Laboratory include the following:
Fresh Concrete Tests
Fresh Concrete Sampling
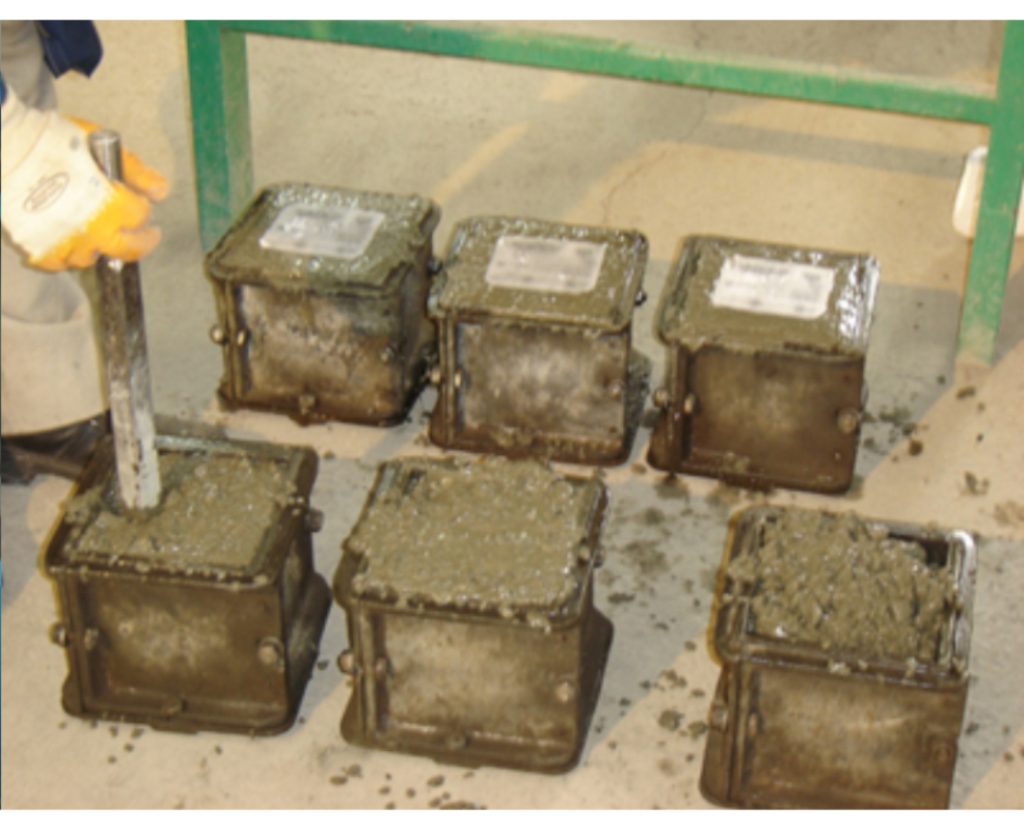



Determination of Concrete Unit Weight

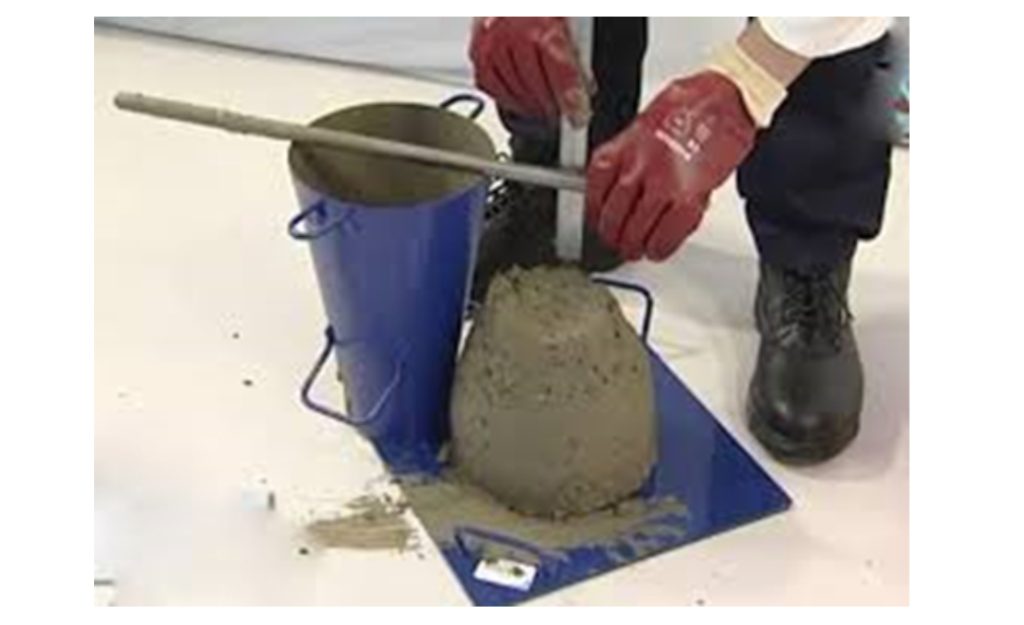
Determination of Concrete Workability by Slump Test

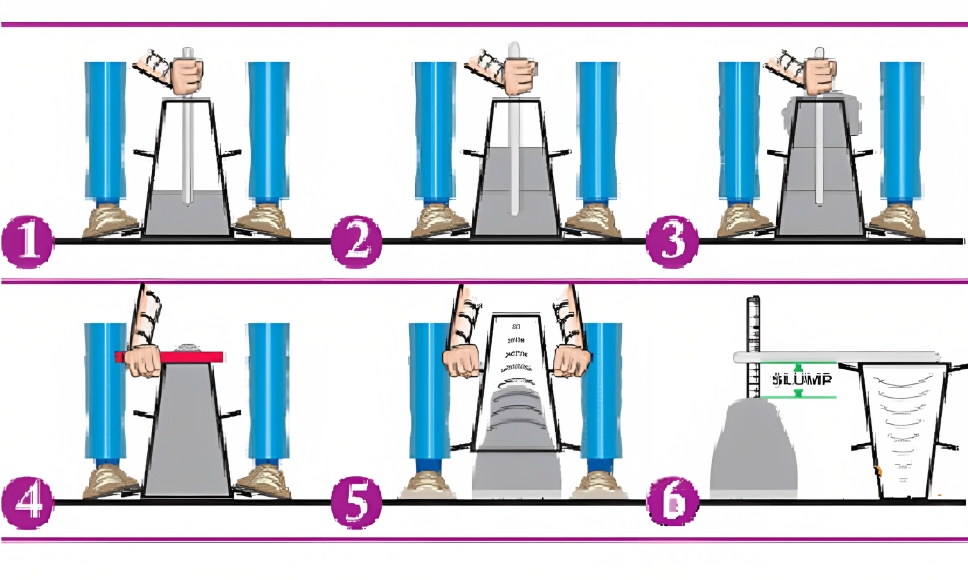
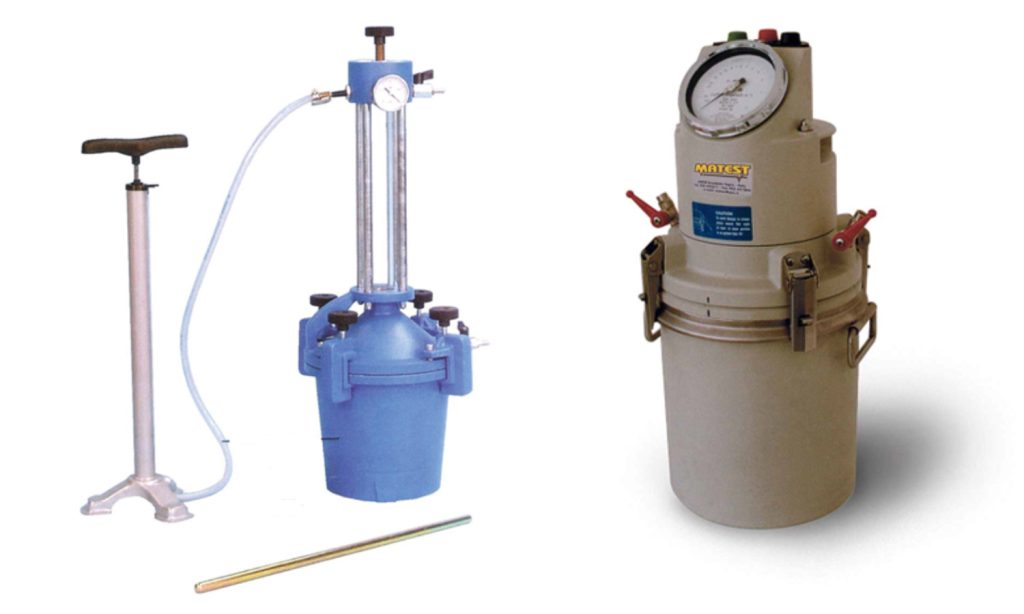
Air Content Test of Concrete by Two Methods

Hardened Concrete Tests
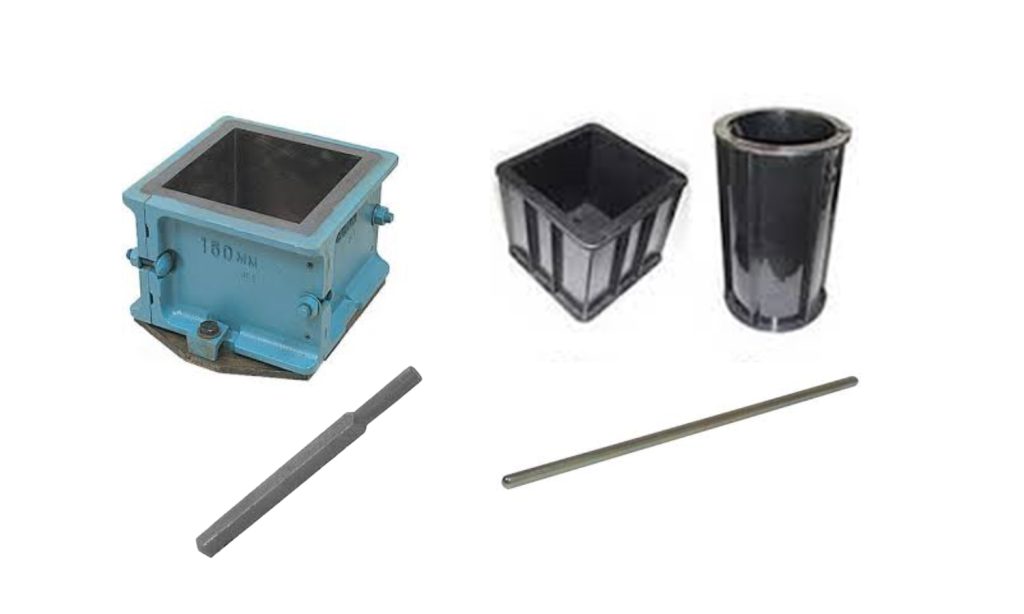
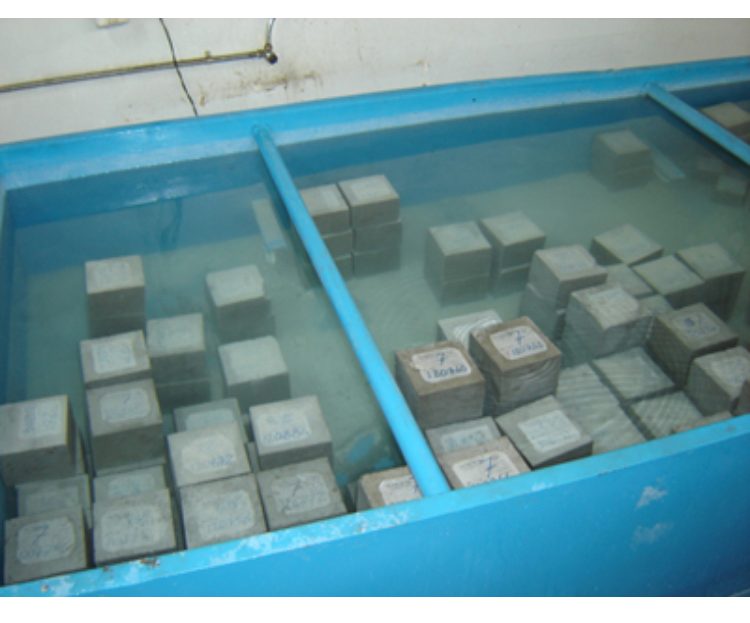
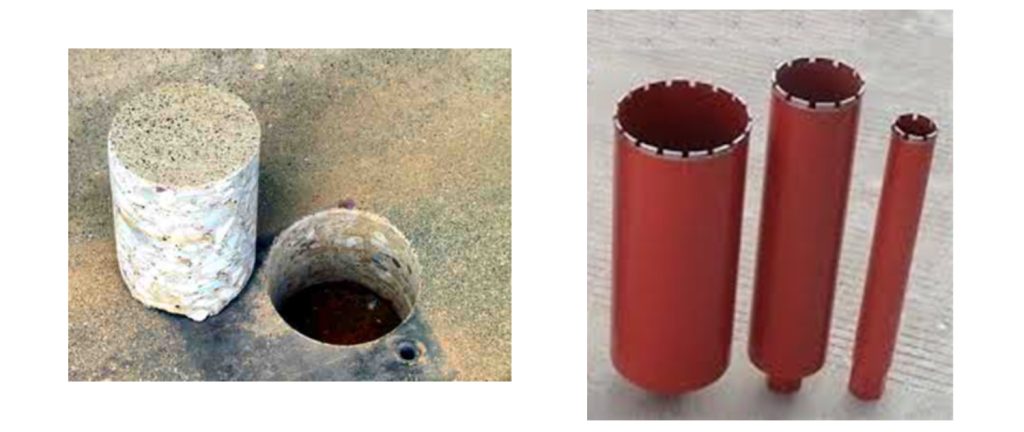
Compressive Strength Determination and Core Sampling
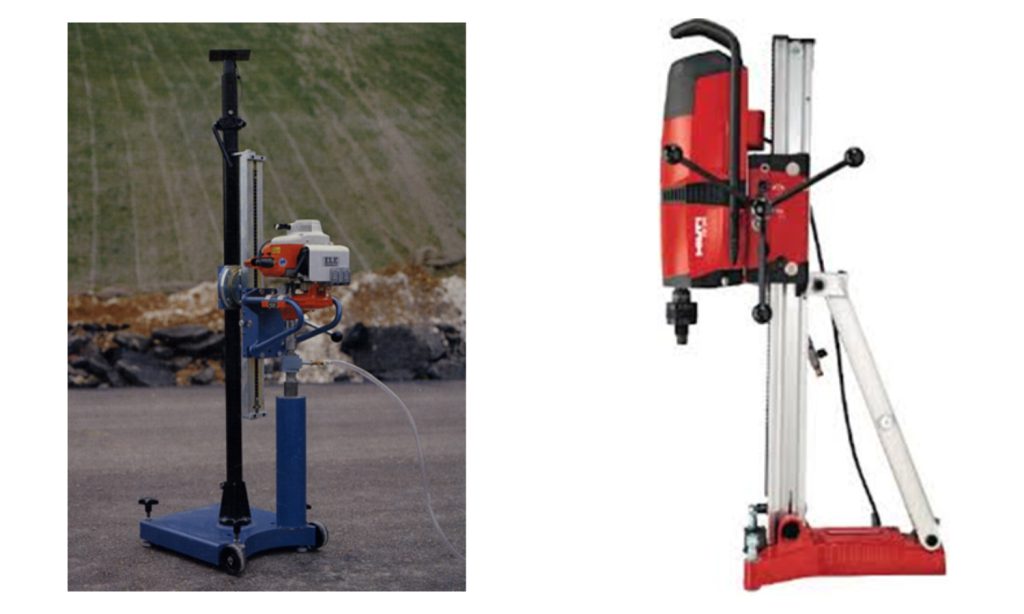


Preparation of Loading Surfaces of Test Specimens
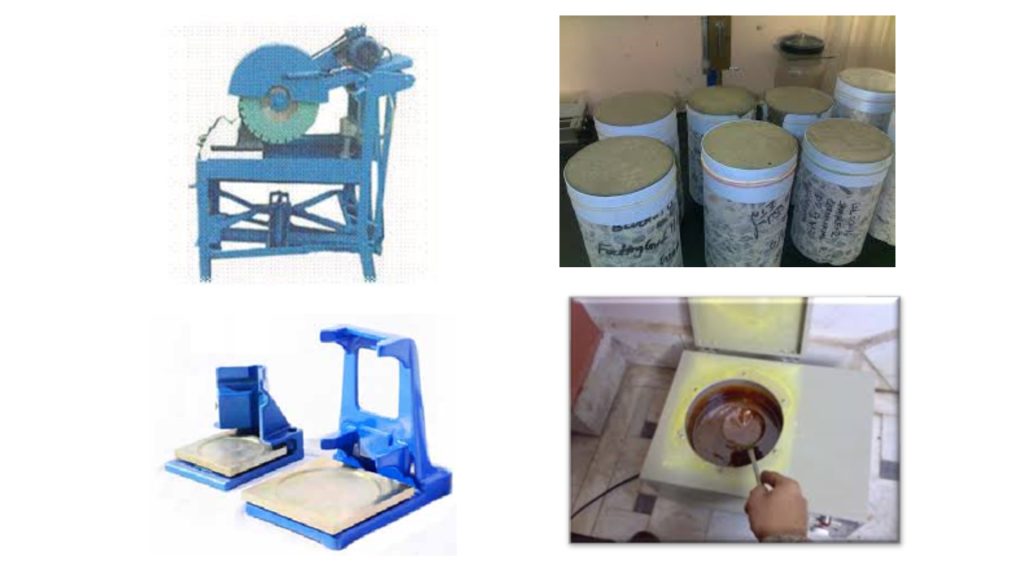

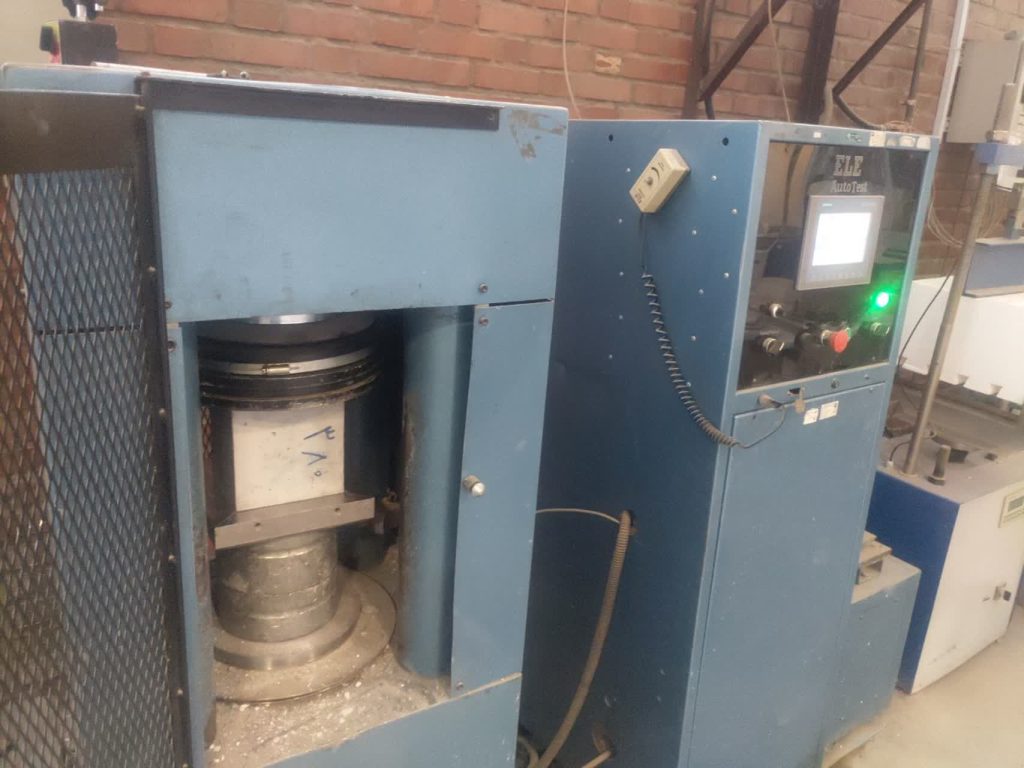
Determination of Compressive Strength of Specimens

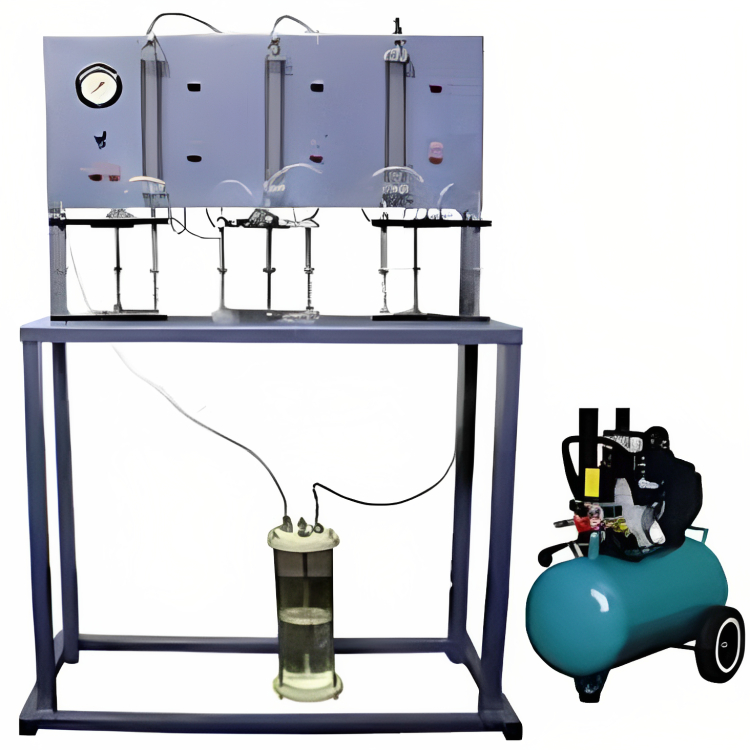
Determination of Water Permeability in Concrete


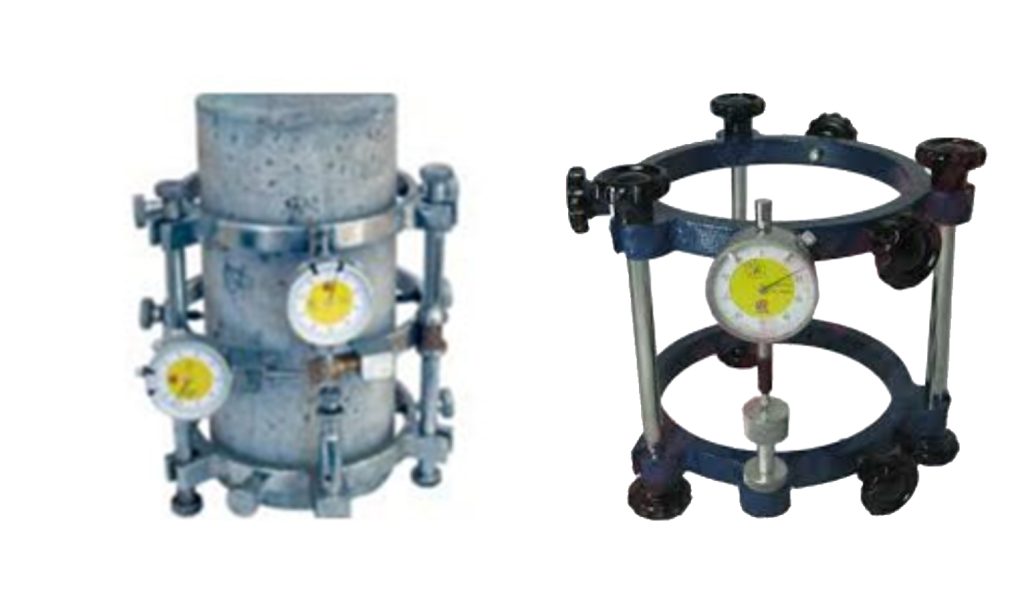
Determination of Elastic Modulus of Concrete

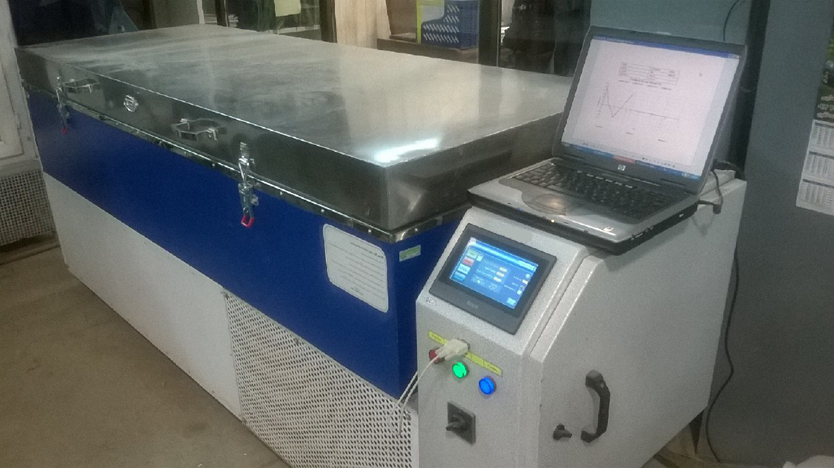
Test for Determining the Resistance of Concrete to Rapid Freezing and Thawing in accordance with ISIRI 12728, ISIRI 755-2, INSO 20185, ASTM C666


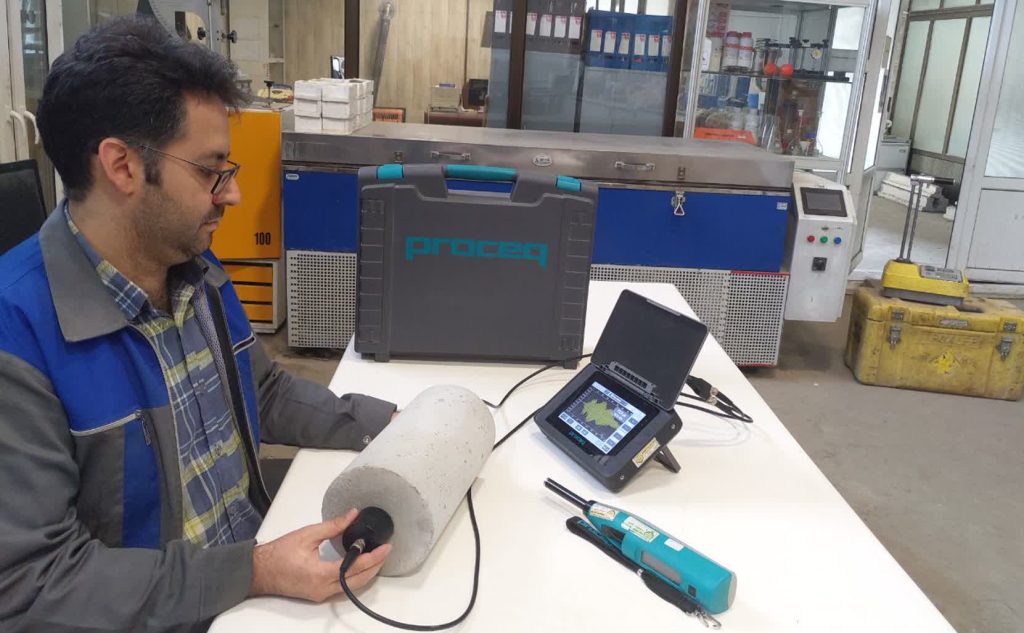
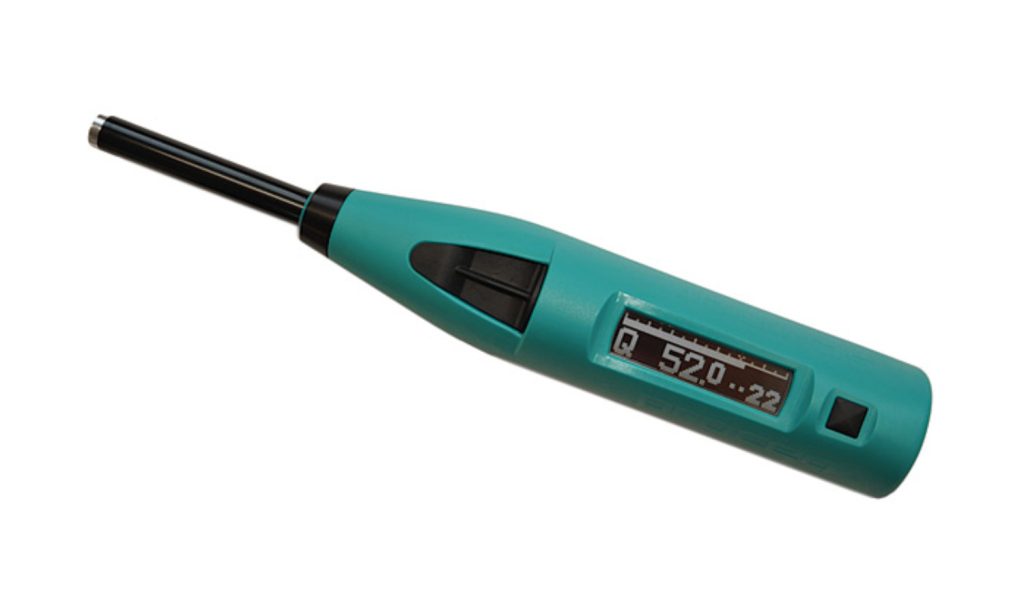
Estimation of Compressive Strength of Hardened Concrete Using the Schmidt Hammer Method
One of the non-destructive tests for concrete that can be performed both on test samples and on constructed structures is the Schmidt Hammer Test (Rebound Hammer Test). This test provides an approximate measure of concrete strength and quality, enabling designers and engineers to make informed decisions regarding strengthening plans, retrofitting, or verifying the accuracy of executed works. One of the non-destructive tests for concrete that can be performed both on test samples and on constructed structures is the Schmidt Hammer Test (Rebound Hammer Test). This test provides an approximate measure of concrete strength and quality, enabling designers and engineers to make informed decisions regarding strengthening plans, retrofitting, or verifying the accuracy of executed works.

Investigating the Effect of Additives on Concrete
- Concrete additives refer to materials that are added to the concrete mix to impart specific characteristics or to enhance its mechanical and physical properties.
- Additives are typically composed of mineral, chemical, or organic substances and can be added to the concrete mix in varying proportions.
- Investigating the effect of additives on concrete is an important area in materials and construction engineering. By using additives, it is possible to improve the properties of concrete and introduce specific characteristics that may enhance its strength, flexibility, heat resistance, or other desirable qualities.
- Extensive studies have been conducted on the effects of additives on the properties of concrete, and this topic continues to be a subject of research in the fields of structural engineering and materials engineering.
- Engineers and researchers are also striving to develop high-performance concretes by utilizing suitable additives, as well as to optimize resource consumption and enhance the sustainability of concrete products.
Concrete Mix Design
Today, concrete is widely used around the world and is regarded as the construction material of the century. Considering the growing trend of development and increasing infrastructure investments in the country, it is essential to give special attention to this important material.
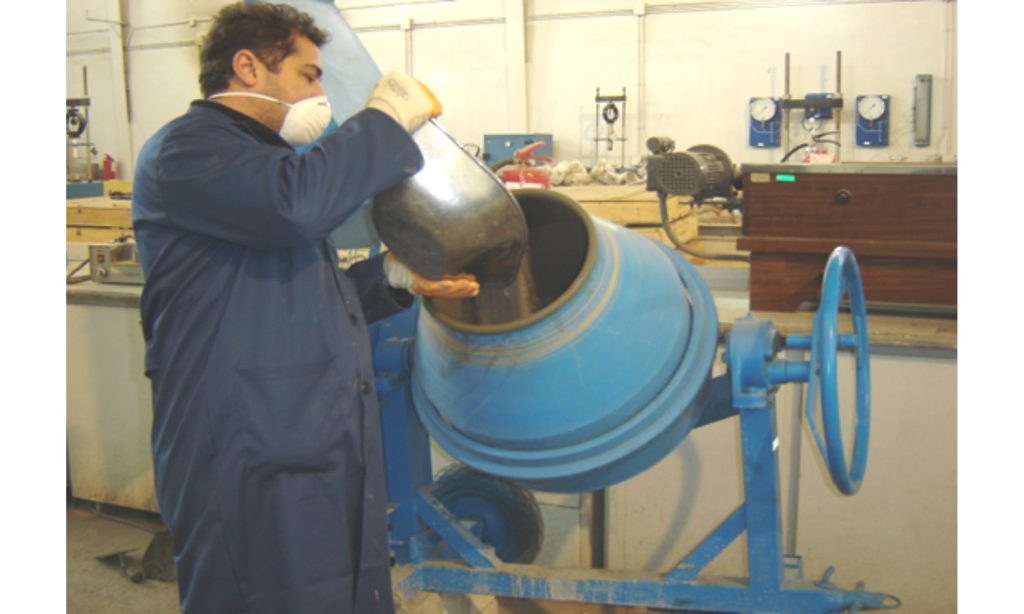
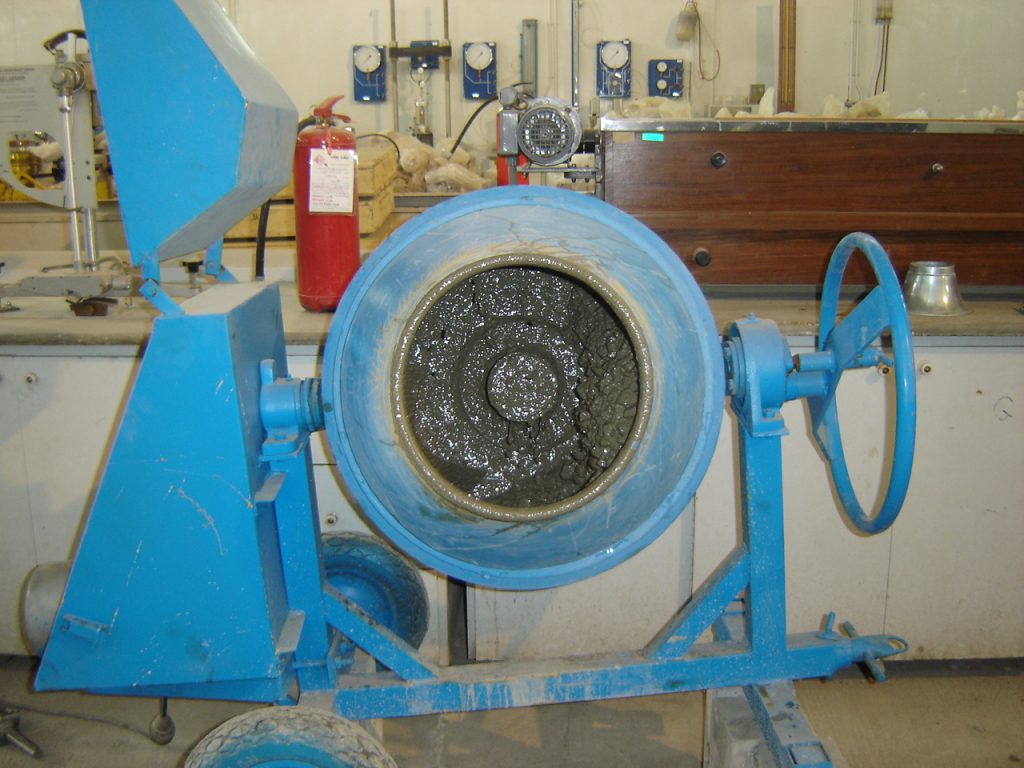


- The proportions of concrete components are determined based on empirical relationships. Mix design refers to the process through which the appropriate combination of concrete components is determined according to given technical specifications.
- The mix design process is complex because changing one variable can have contradictory effects on the properties of concrete.
- For example, adding water to a low-workability concrete mix may increase its fluidity but reduce its strength.
- In fact, workability consists of two main components: fluidity and cohesiveness. When water is added to the mix, these two characteristics may exhibit opposing effects.
- Therefore, mix design is the art of balancing these opposing effects.
- Since the construction of concrete elements and structures that meet technical requirements and desired durability, while remaining economical, depends entirely on an appropriate concrete mix design, achieving optimal results requires conducting necessary tests and examining the physical properties of the aggregates. These properties include grading, sand equivalent value, determination of sand fineness modulus, specific gravity (bulk, apparent, and saturated surface-dry), water absorption percentage, and more. Based on these evaluations, the mix design is carried out according to the method... ACI 211.1 which is one of the most efficient and reliable concrete mix design methods worldwide and is used as the standard in most international projects.
Concrete Aggregate Testing
Concrete aggregate testing includes the following items:
- Mechanical Sieve Analysis of Aggregates
- Determination of Harmful Materials in Aggregates
- Durability of Aggregates Against Weathering Factors
- Determination of Aggregate Void Content
- Determination of Aggregate Abrasion Percentage
- Determination of Sand Equivalent
- Determination of Aggregate Fracture Percentage
- Determination of Bulk Density
- Density and Water Absorption of Aggregates
- Determination of Alkali-Silica Reaction (ASR) Potential of Aggregates
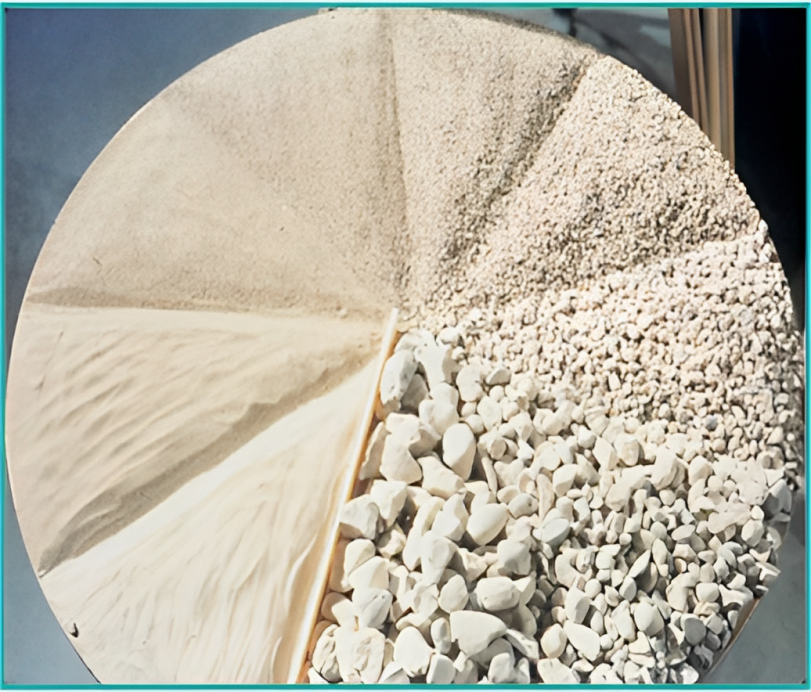
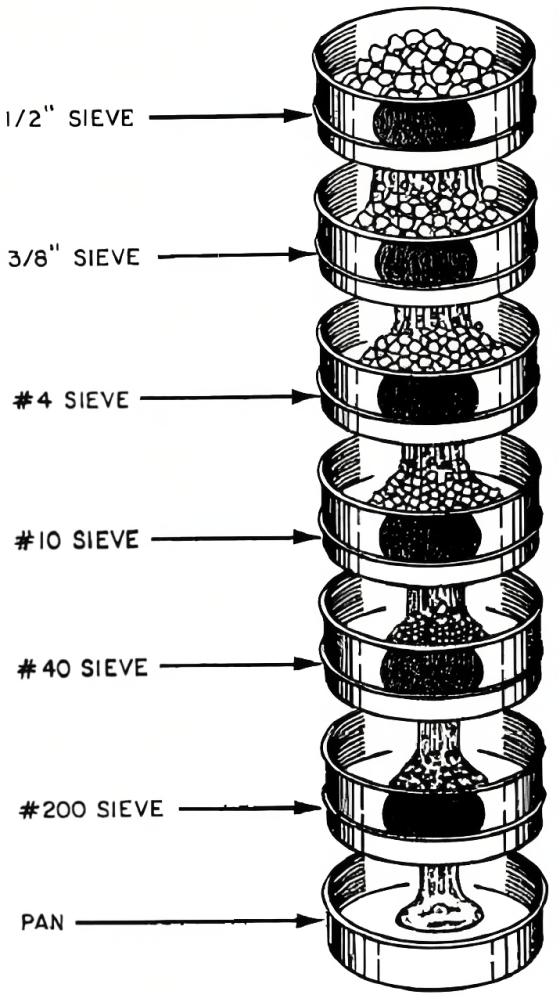

Aggregate Tests
Building Materials Testing
- Clay Brick Tests According to INSO 7 Standard

- Non-Load-Bearing Cement Block Tests According to INSO 7782 Standard

- Tests for Lightweight Non-Load-Bearing Panels and Clay Bricks with Horizontal Holes According to ISIRI 7122 Standard

- Tests for Clay and Concrete Roof Blocks According to ISIRI 2909-2 Standard

- Tests for Polystyrene Roof Blocks According to INSO 11108 Standard

- Tests for Mosaic Tiles According to ISIRI 755-1 and 755-2 Standards

- Tests for Autoclaved Aerated Lightweight Concrete According to ISIRI 8593 Standard

- Tests for Trussed Joists According to ISIRI 2909-1 Standard

- Tests for Precast Concrete Curbs According to ISIRI 12728 Standard

- Tests for Concrete Paving Blocks According to National Standard INSO 20185

Conducting tests related to concrete mixing water
Tests for Concrete Mixing Water include the following items:
- Sulfate Determination
- Chloride Determination
- pH Determination
- Determination of Soluble Materials
- Determination of Suspended Solids
- Determination of Alkalinity
Performing Tests Related to Cement
- Comprehensive physical, chemical, and mechanical tests of cement are conducted at the Arman Sanat Tadbir Andish laboratory complex.

Determination of Flexural Strength of Curbs
Abrasion Resistance Test for Curbs and Mosaic Tiles
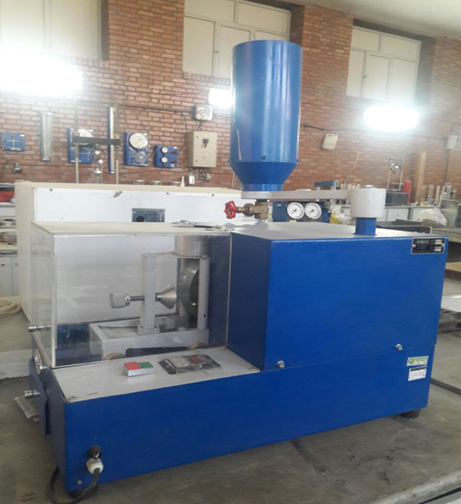

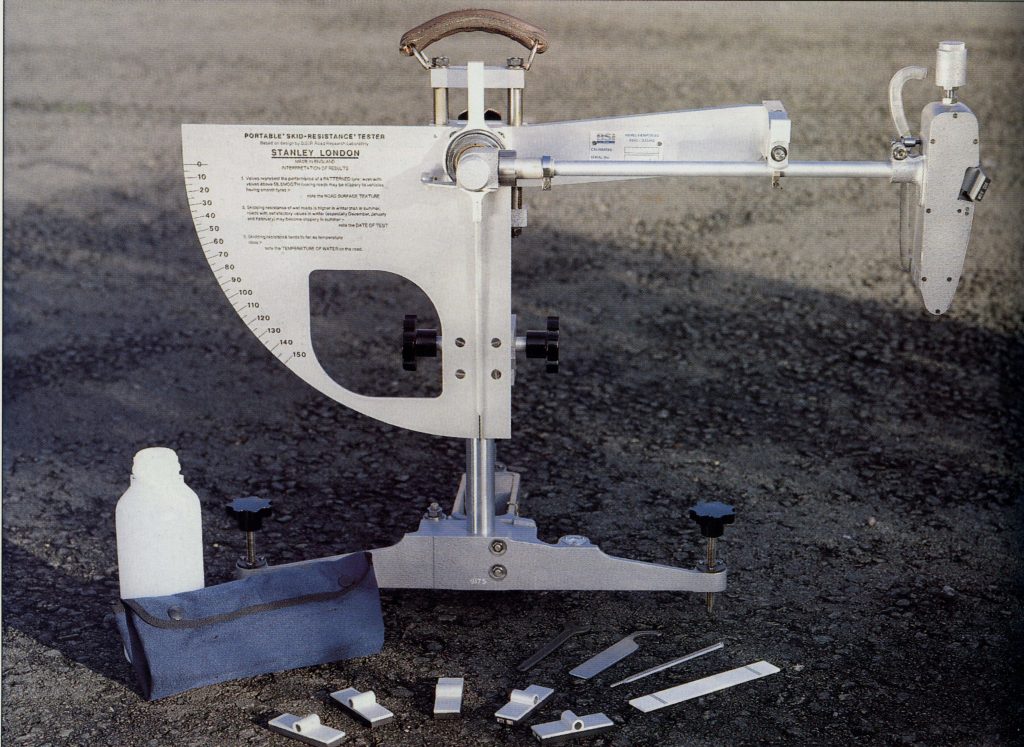
Friction Resistance Test for Curbs, Mosaic Tiles, and Paving Blocks According to Standards ISIRI 12728, ISIRI 755, and INSO 20185

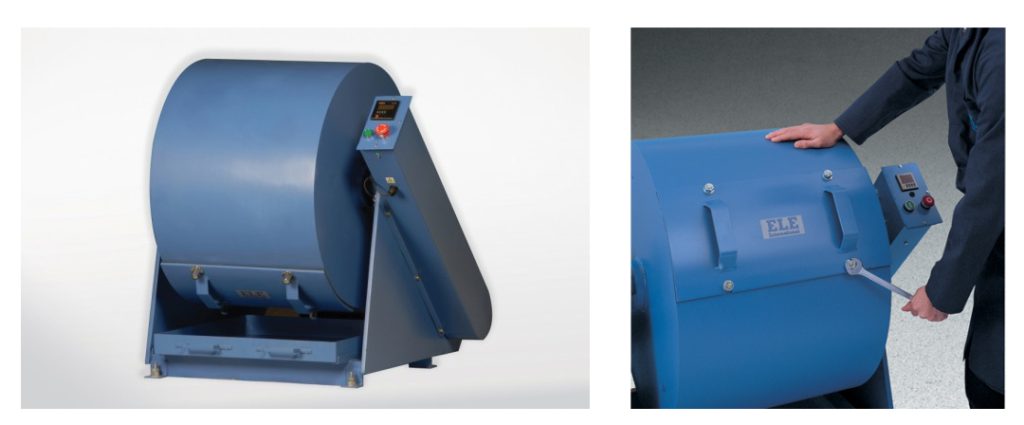
Test for Determining the Abrasion and Impact Resistance of Aggregates Using the Los Angeles Machine

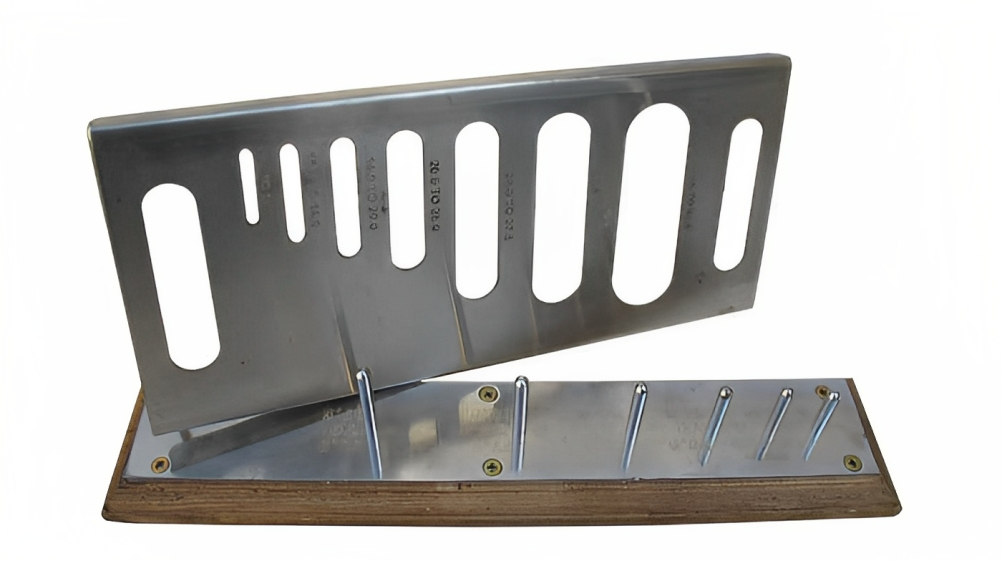
Test for Determining the Percentage of Elongated or Flaky Aggregates
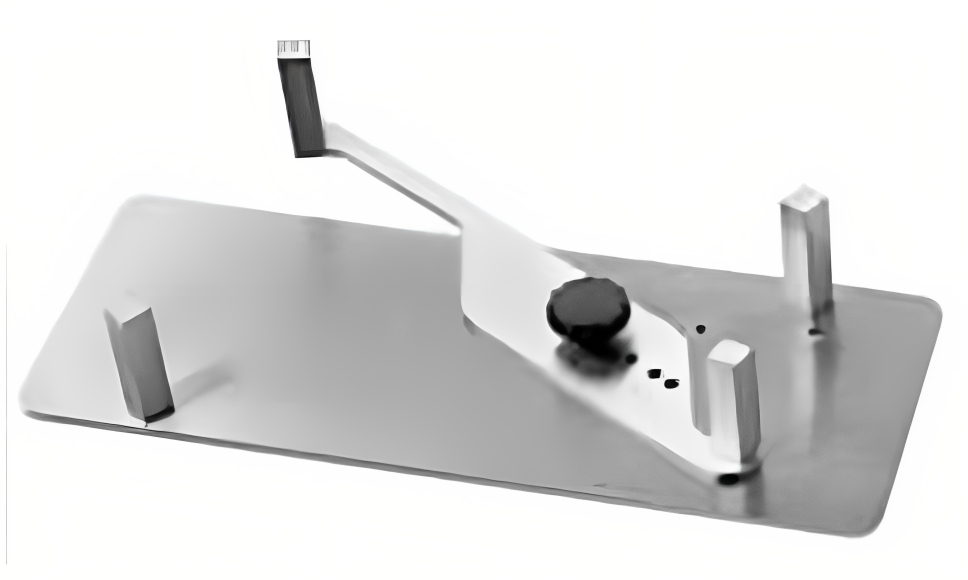


Test for Determining the Reactivity of Siliceous Aggregates with Alkalis Using the Accelerated Mortar Bar Method

Joist Load Testing

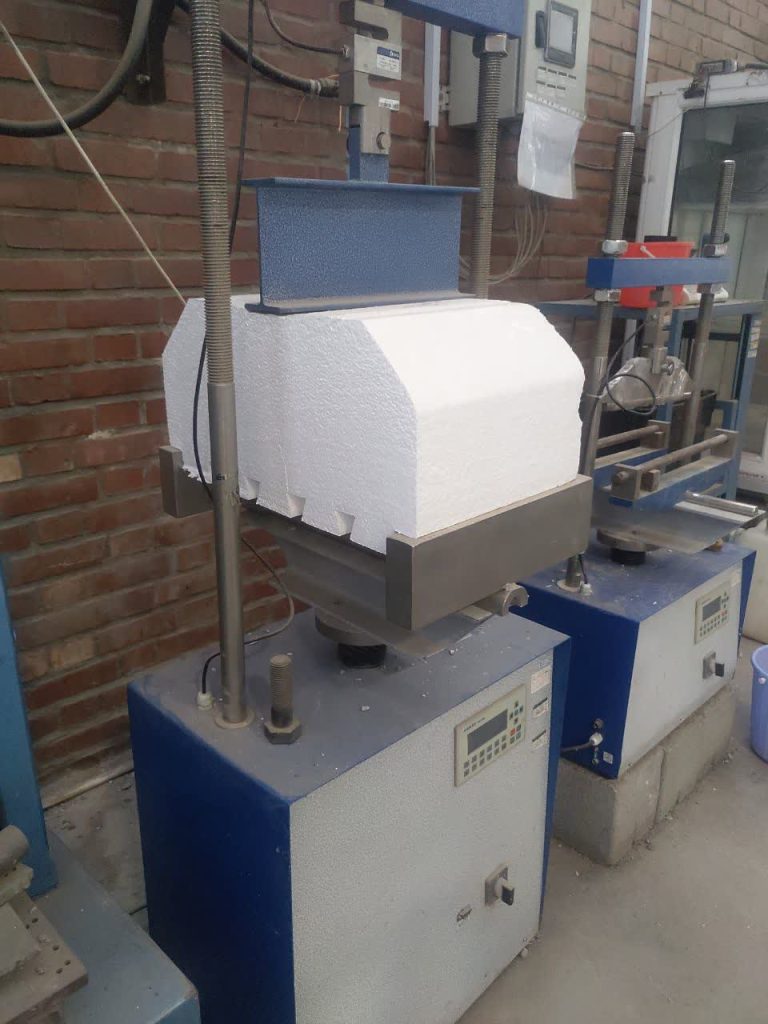
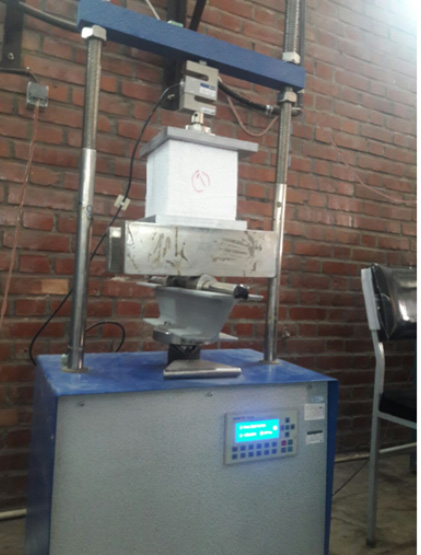
Test for Determining the Flexural and Compressive Strength of Polystyrene Roof Blocks


Test for Determining the Fire Resistance of Polystyrene under Direct Flame Exposure

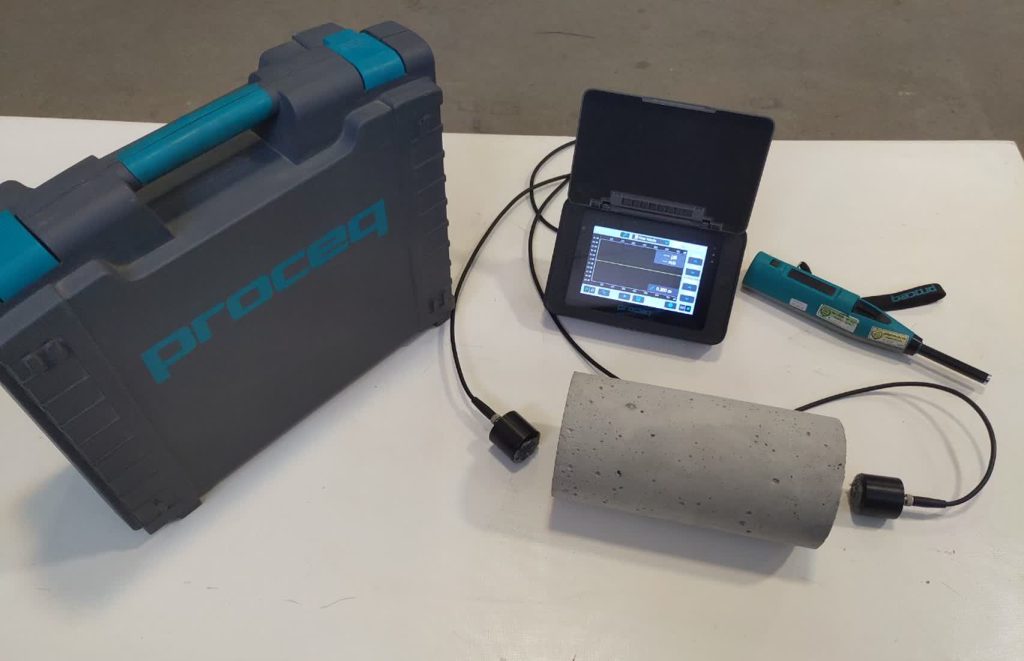
Investigation of Hardened Concrete Using the Ultrasonic Method

